The CIA Triad
confidentiality, integrity, availability is important for information security. These 3 components should be present in a secure system.
- confidentiality is a component of privacy that implements to protect our data from unauthorized viewers.
- integrity means to maintain the consistency, accuracy and trustworthiness of data over its entire life cycle.
- availability - all the information should be available and accessible for authorized persons .
Encoding
Encoding is not really cryptography, it is a technique of converting data from one form to another.
It is reversible.
Types Of Encoding
- Character encoding
In it characters are encoded as bytes. Since computers only recognize binary data, text must be represented in a binary form. This is accomplished by converting each character (which includes letters, numbers, symbols, and spaces) into a binary code.
Common types of text encoding include ASCII and Unicode.
-
American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) is a character encoding that uses numeric codes to represent characters. These include upper and lowercase English letters, numbers, and punctuation symbols. Keyboard keys are also mapped to standard ASCII values.
ASCII codes may also be displayed as hexadecimal values instead of the decimal.
It does not support all languages (Asian).
Example: Escape key (ESC) is 27 and it's hex is 1B. -
Unicode Transformation Format (UTF) refers to several types of Unicode character encodings, including UTF-7, UTF-8, UTF-16, and UTF-32.
Unicode = Universal Character Code
It was designed beacuse ASCII was not able to cover all the characters.
It is used to encode text in webpages.
- UTF-8 - the most popular type of Unicode encoding. It is backwards compatible with ASCII. It uses:
- 1 byte for standard English letters and symbols,
- 2 bytes for additional Latin and Middle Eastern characters, and
- 3 bytes for Asian characters.
- 4 bytes for Additional characters.
Demo:
To find out encoding present in a webpage:
Right click> View/Page source> Open HTML of the page
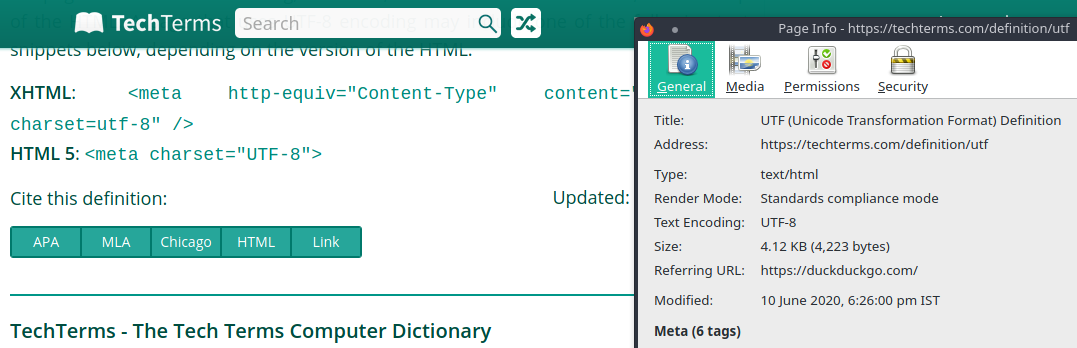
A page that uses UTF-8 encoding may include one of the following text:
In HTML 5:
<meta charset="UTF-8">

OR
Right click>Page Info
- Base Encoding
In it binary data is converted to ASCII.
It is used when binary data, such as images or video, needs to be transmitted in a plain-text (ASCII) format.
Binary
Binary is 0 or 1 which represents state of electricity in the microchips (1=ON , 0=OFF).
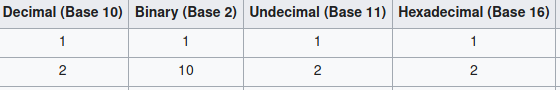
We use base10 (decimal) numerical system.
Means the numbers are made of 10 symbols from 0 to 9.
All base systems works on positional notation.
Means we put a number at the left side.
Like in base10 when we get to a number divisible by 10 we add a digit (1) to the left.
Each new value will be 10 times greater.
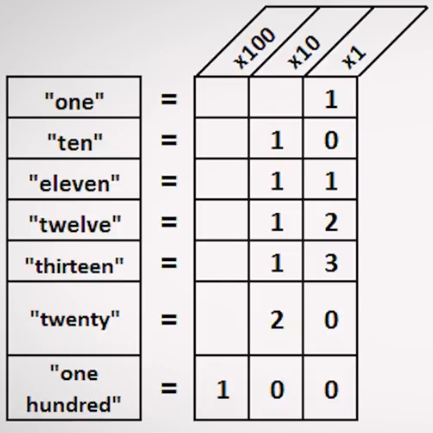
All base systems after base10 are AlphaNumeric (uses Alphabets to represent numbers > 9).
Base2 (Binary)

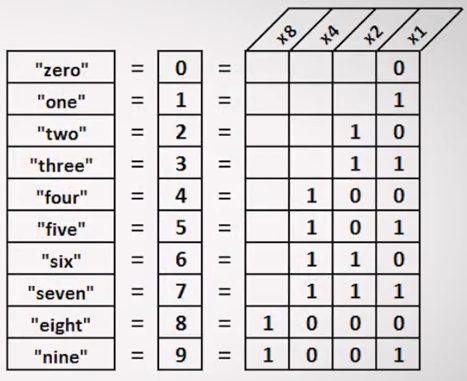
155 represented in Base2
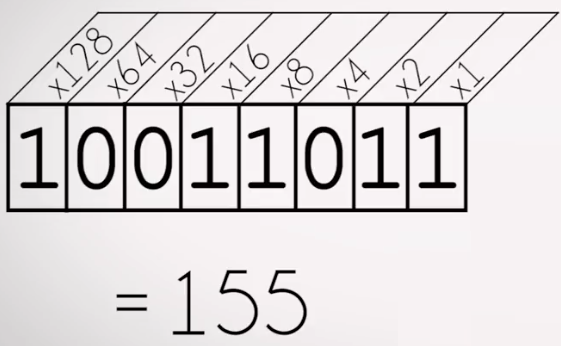
Sum only those which are ON (have 1).
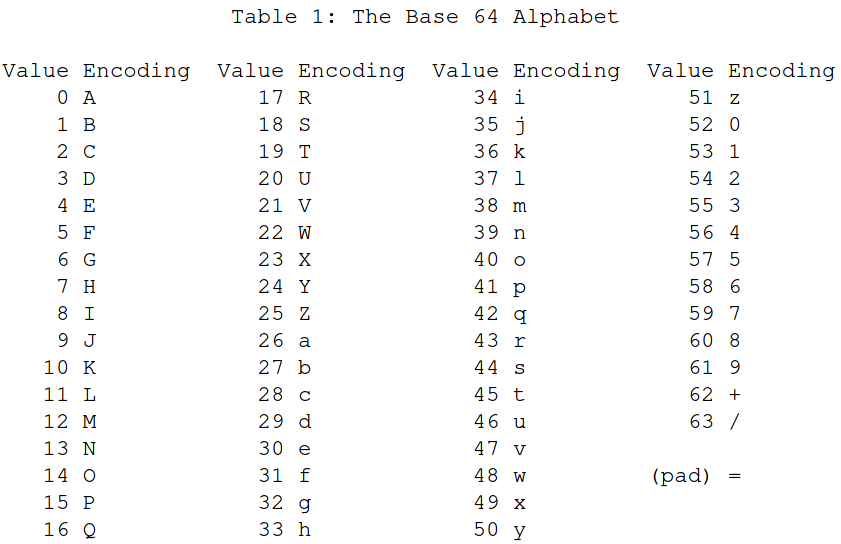
Base64
2^6 = 64 characters
Binary data is broken into 6-bit segments and then converted to ASCII characters using the table.
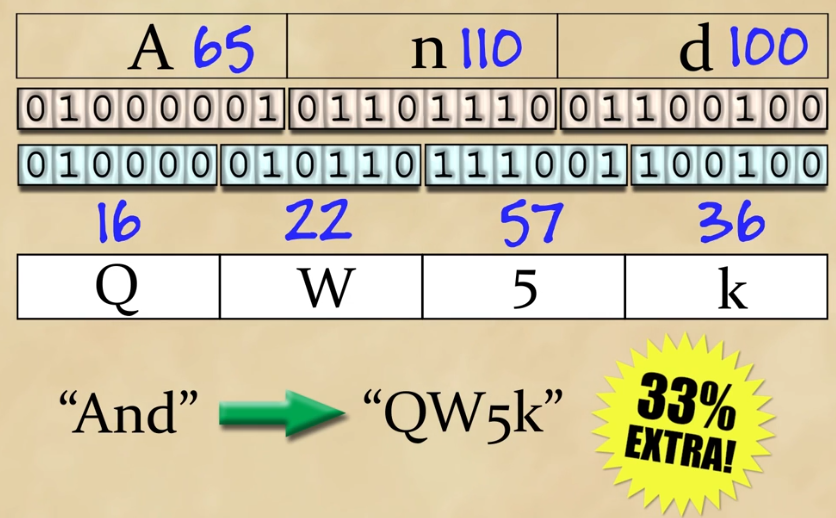
In ASCII, A = 65 same for n & d.
We break 'AND' into binary,then those binaries into 6 bits and then the result into ASCII and map ASCII chars with base64 table to obtain the base64 values.
Note: A base64 encoded string doesn't always end with a =, it will only end with one or two = if they are required to pad the string out to the proper length.
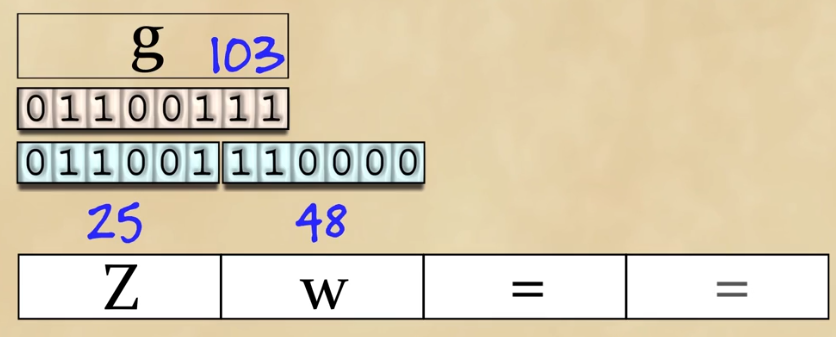
Base64 encoding, decoding
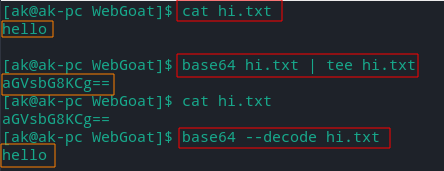
- Basic Authentication in http uses base64 in the HTTP header:
Authorization: Basic bXl1c2VyOm15cGFzc3dvcmQ=
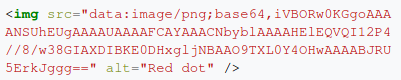
- It is also used on the web to encode binary data so that it can be included in a data: URL.
data:[<mediatype>][;base64],<data>
data:URL are used to include in-line data in HTML webpages like a image.
Example:
An image of a small red dot.
- URL Encoding
URLs can only be sent over the Internet using the ASCII character-set. If a URL contains characters outside the ASCII set, the URL has to be converted.
-
URL encoding converts non-ASCII characters into a format that can be transmitted over the Internet.
-
URL encoding replaces non-ASCII characters with a "%" followed by hexadecimal digits.
-
URLs cannot contain spaces. URL encoding normally replaces a space with a plus (+) sign, or %20.
- HTML Form Encoding
It is used when sending form data and request parameters to the server.
The encoding type of a form is determined by the attribute enctype, which has 3 values:
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded - Represents an URL encoded form. This is the default value if enctype attribute is not set to anything.
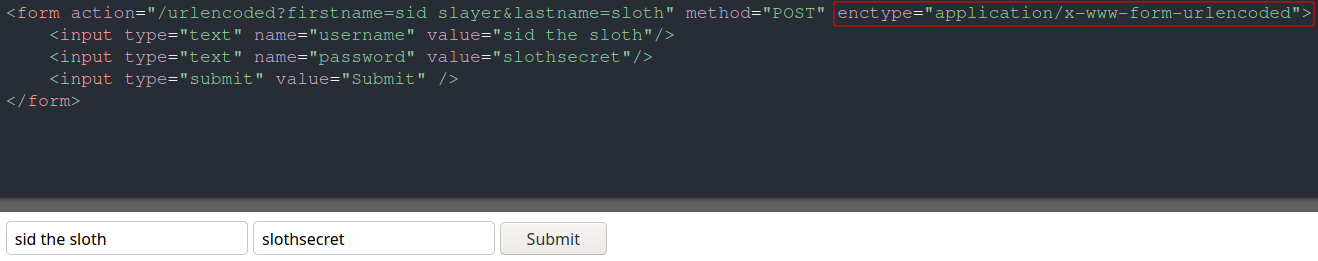
Above, the form is submitted using POST request.
The action attribute specifies where to send the form-data when a form is submitted.
The & ampersand acts as a delimiter between each (name, value) pair, enabling the server to understand when and where a parameter value starts and ends.
A delimiter is one or more characters that separate text strings.
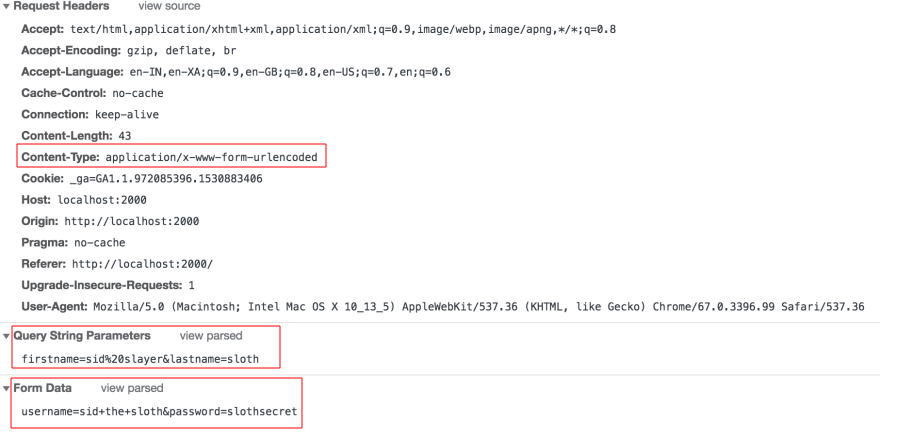
Chrome represents form fields under Form Data.
And as we can see the spaces in URL are encoded (replaced by either '%20' or '+').
- multipart/form-data - Represents a Multipart form. This type of form is used for uploading files.
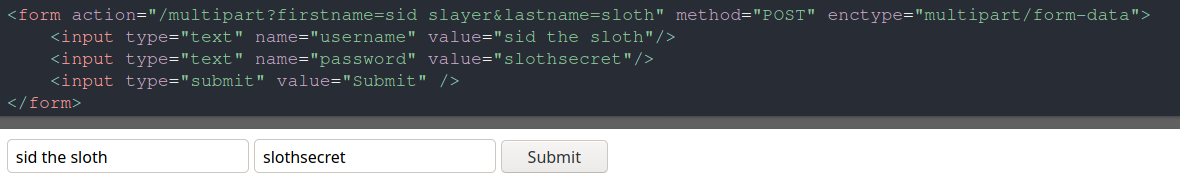
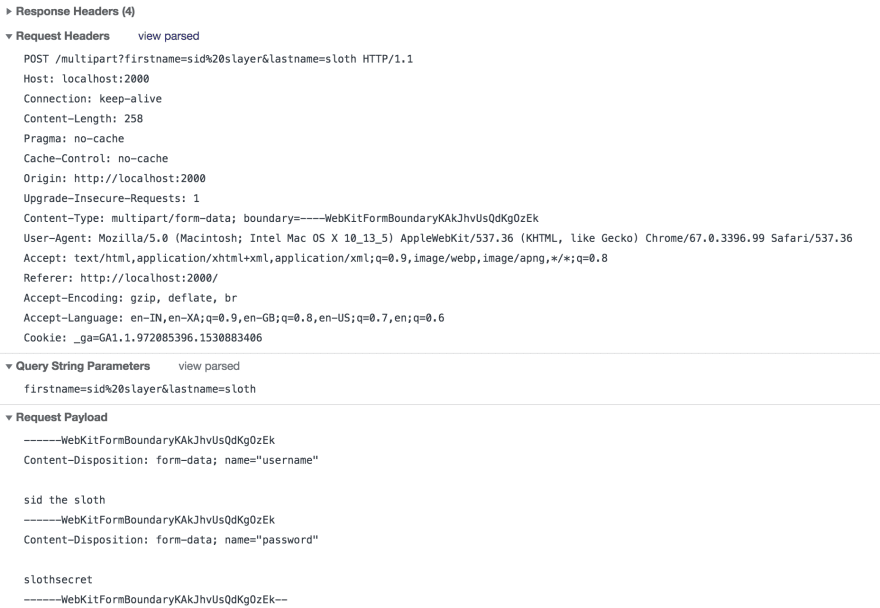
In content-type header the boundary value tells the server to understand when and where a parameter value starts and ends.
Request Payload contains the form fields.
The entire payload is terminated by the boundary value suffixed with a --.
The hyphens themselves are not part of the boundary value but rather needed as part of the request format.
- text/plain - sends the data without any encoding
- UUEncode
The Unix-2-Unix encoding is used to encode data for transmission in mediums that only support ASCII data like emails.
It has now been largely replaced by MIME and yEnc.
- Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is an Internet standard that enables email messages to support non-ASCII characters, as well as attachments of audio, video, images, and application programs.
It was designed for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) but is also used in other protocols like HTTP.
Browsers use the MIME type to determine how to process a URL.
- XOR encoding
Used to store passwords in configuration files. Used by IBM WebSphere Application Server.